Digital Scalable Production with 3D Printing
Digital Scalability in Production: A Guide for companies towards sustainable growth
In the ever-evolving landscape of the manufacturing sector, the ability to adapt and grow flexibly has become a key factor for success.
In this scenario, Digital Scalable Production emerges as a winning strategy for companies leveraging 3D printing services, offering numerous advantages in terms of competitiveness and sustainability
What is scalable manufacturing?
Scalable manufacturing is the ability of a company to increase or decrease production based on market needs, without compromising efficiency, quality or profitability.
In other words, it is a flexible and adaptable production system that allows us to respond promptly to fluctuations in demand.


Vanna Menco, CEO of Prosilas, underscores the importance of this approach:
“Scalable production is not just a matter of economic efficiency, but represents a true paradigm shift that enables companies to adapt to demand fluctuations and respond quickly to market needs.”
Why Scalable Production Is Important for Companies?
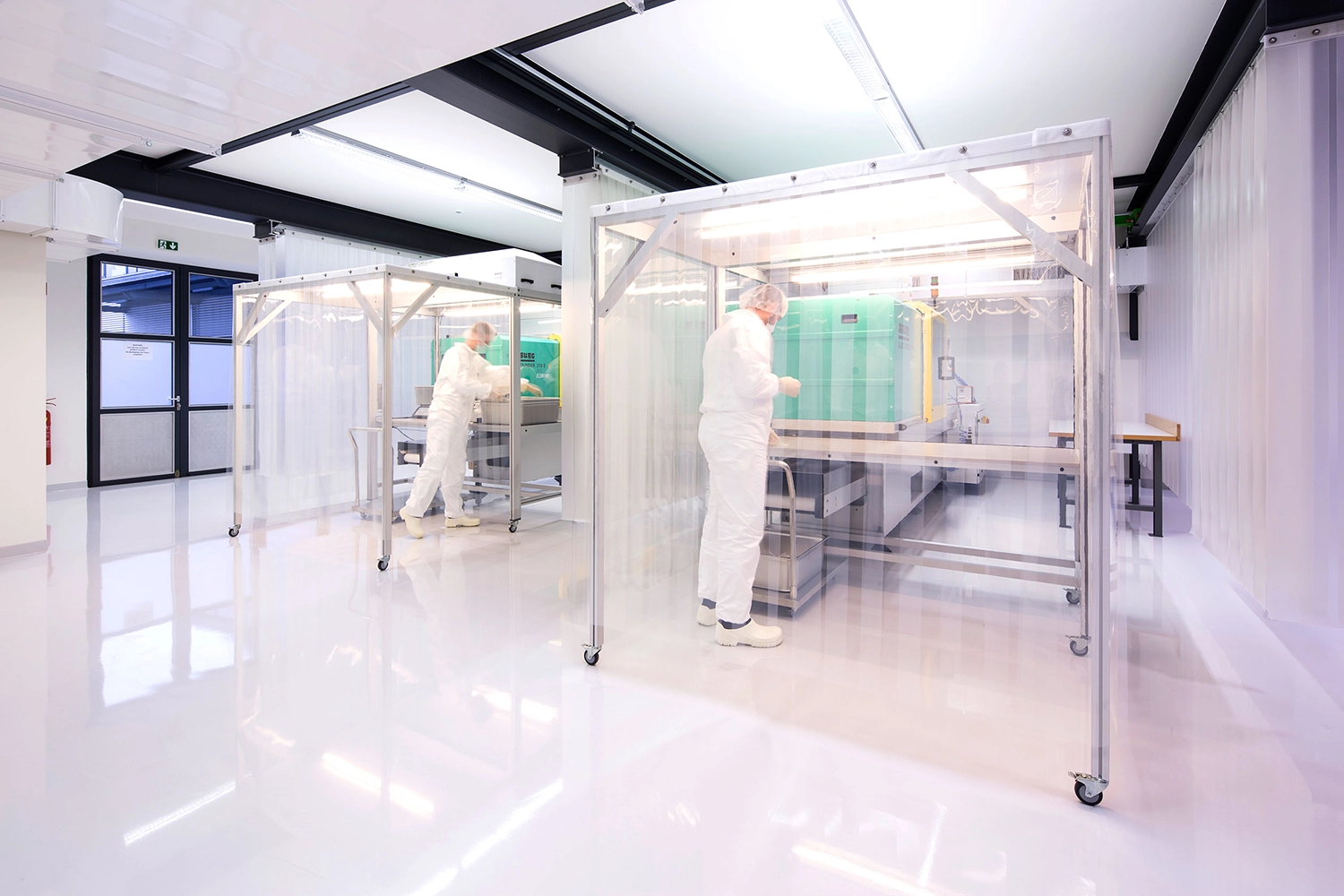
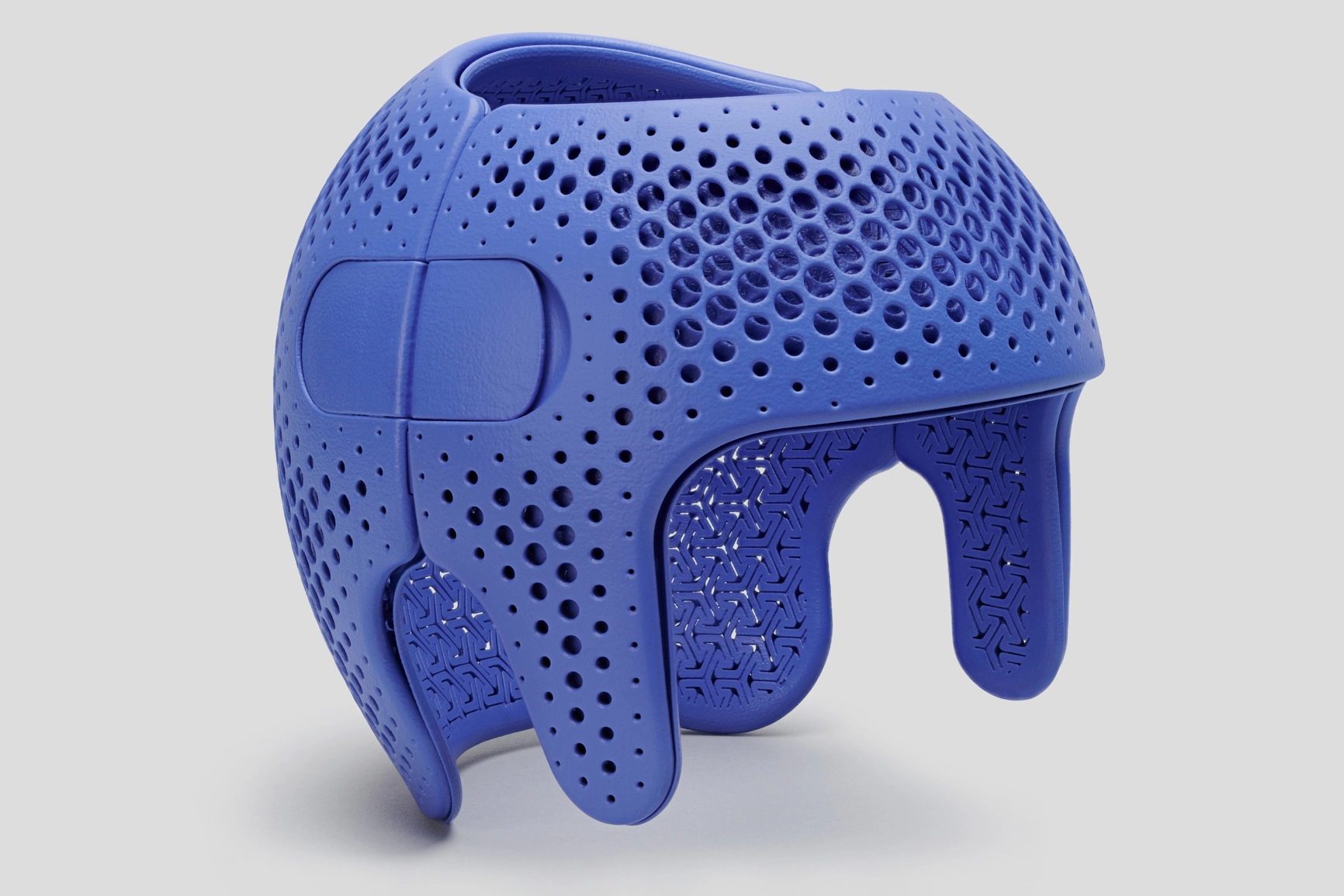
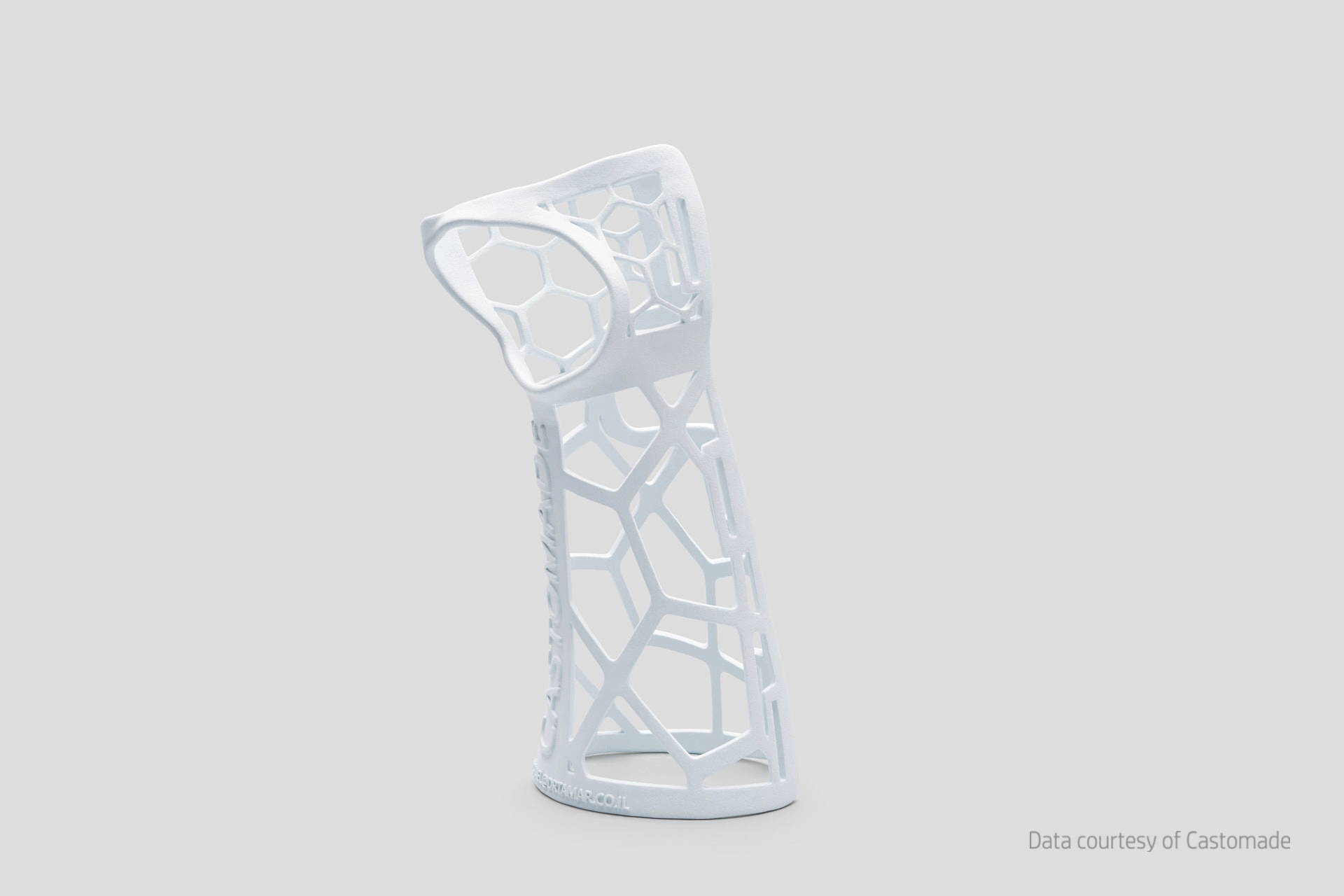
3D printing is particularly suited to a scalable production model, offering numerous advantages to companies:
- Flexibility and adaptability: 3D printing allows for rapid transition from prototype to mass production and enables the modulation of production according to market needs without drastically altering production processes. This is crucial for companies operating in constantly evolving markets that need to promptly respond to demand fluctuations.
- Efficiency and profitability: 3D printing optimizes resource utilization, reduces waste, and accelerates delivery times. This results in increased efficiency and profitability for companies.
- Sustainability: 3D printing contributes to a more eco-friendly production model by reducing material usage and environmental impact.
Investing in the Future with 3D Printing
Embracing a scalable production approach means investing in the future of one’s company. Companies that leverage this model will be able to:
- Stay competitive: The flexibility and adaptability of scalable production allow companies to remain competitive in an ever-changing market.
- Reduce risks: Waste reduction and resource optimization minimize financial risks and improve profitability.
- Invest in development: Scalable production frees up resources that can be invested in the development of new products and services.
- Promote sustainability: 3D printing contributes to a more environmentally friendly production model, reducing the company’s environmental impact.