It represents a three-dimensional geometry by means of a combination of triangles unfolding in three-dimensional space.
NEW SPARE PARTS AND SPARE PARTS: 3D PRINTING FOR THE HYDRAULIC SECTOR.
The opportunities offered by 3D printing are now multiple and the continuous developments of technology allow us to respond promptly even to the needs of sectors that were considered too specific such as hydraulics and hydrothermohydraulics.
An innovative solution
In particular, the innovative combination of industrial 3D scanning and 3D printing with SLS tencology offers a wide range of opportunities. In particular, in the hydro-hydraulic sector, the production of implementation and replacement parts on furniture, taps, sanitary ware, air conditioning and convector systems represent one of the greatest challenges and needs.
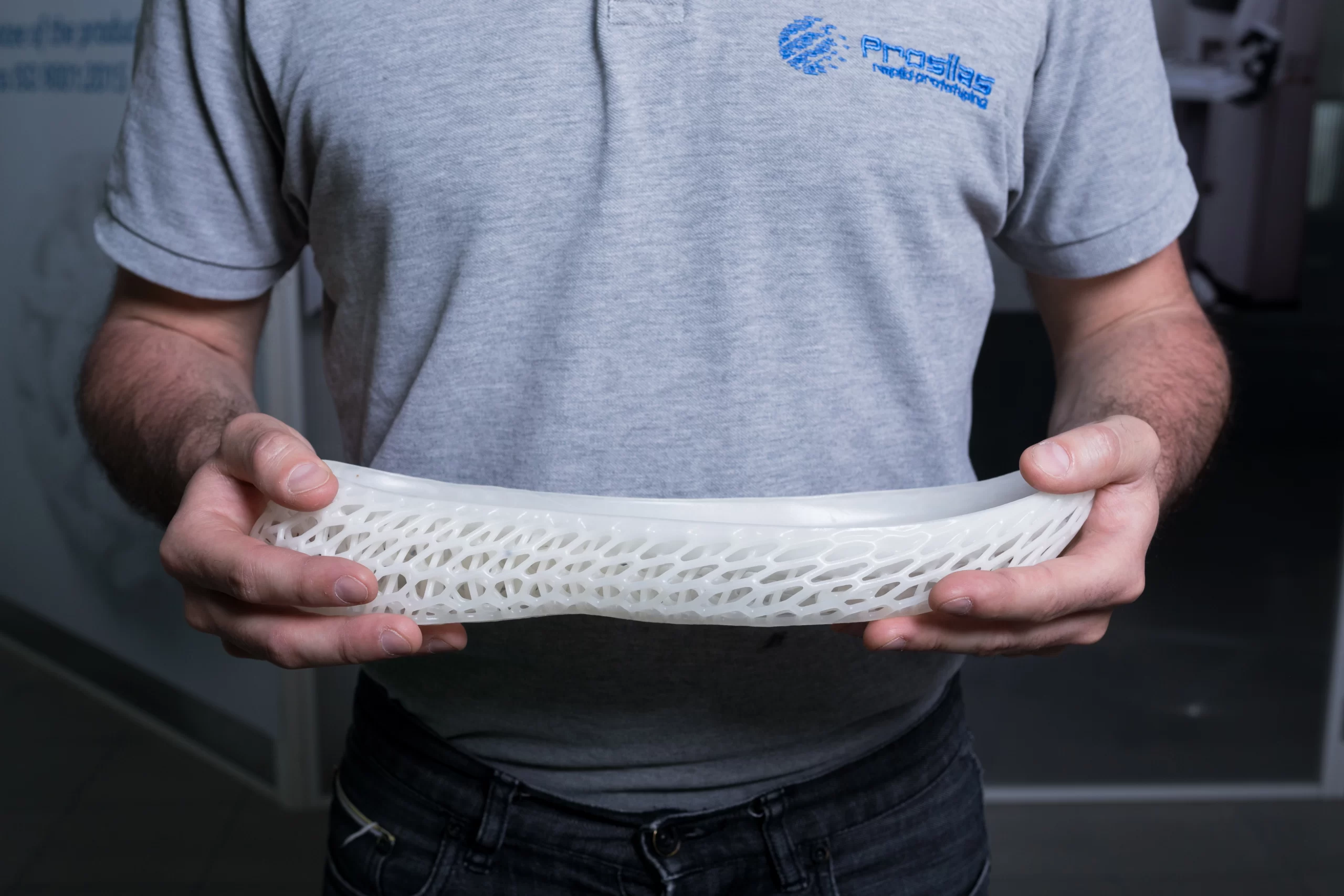
It is precisely here that additive manufacturing represents an excellent alternative, with numerous advantages over more traditional technologies, both from the point of view of the aesthetic and mechanical performance guaranteed on the parts produced, both for its ability to reproduce obsolete or discontinued components, intervening if necessary on the optimization of geometries quickly and functionally .


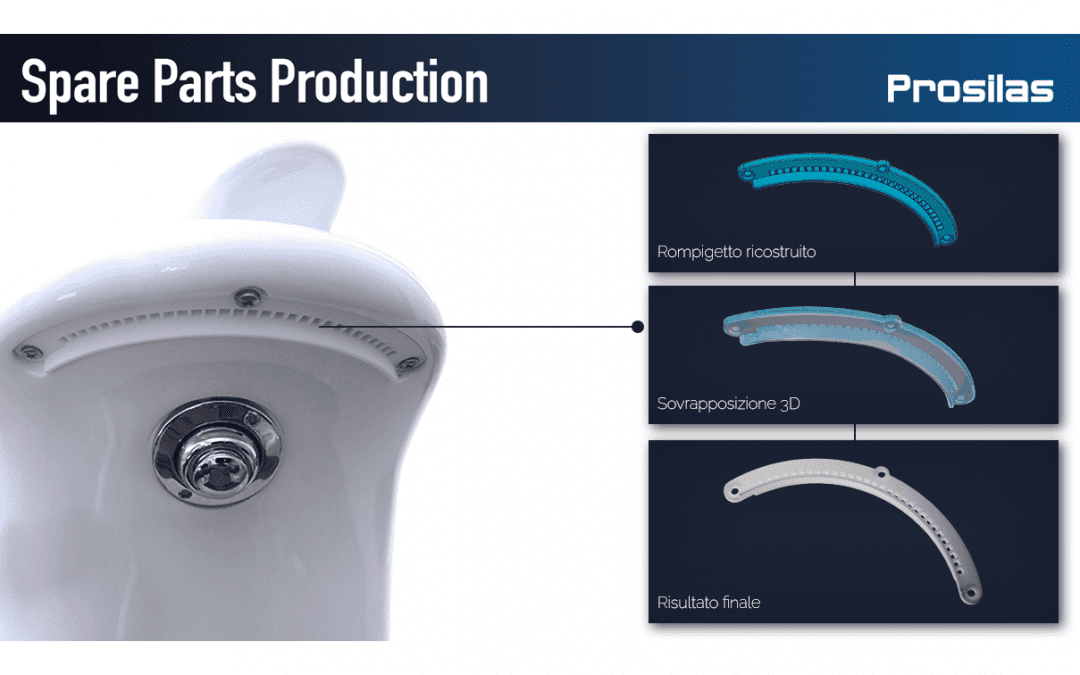
Rebuilding spare parts that are now out of production or whose mold has been lost has never been so simple and fast!
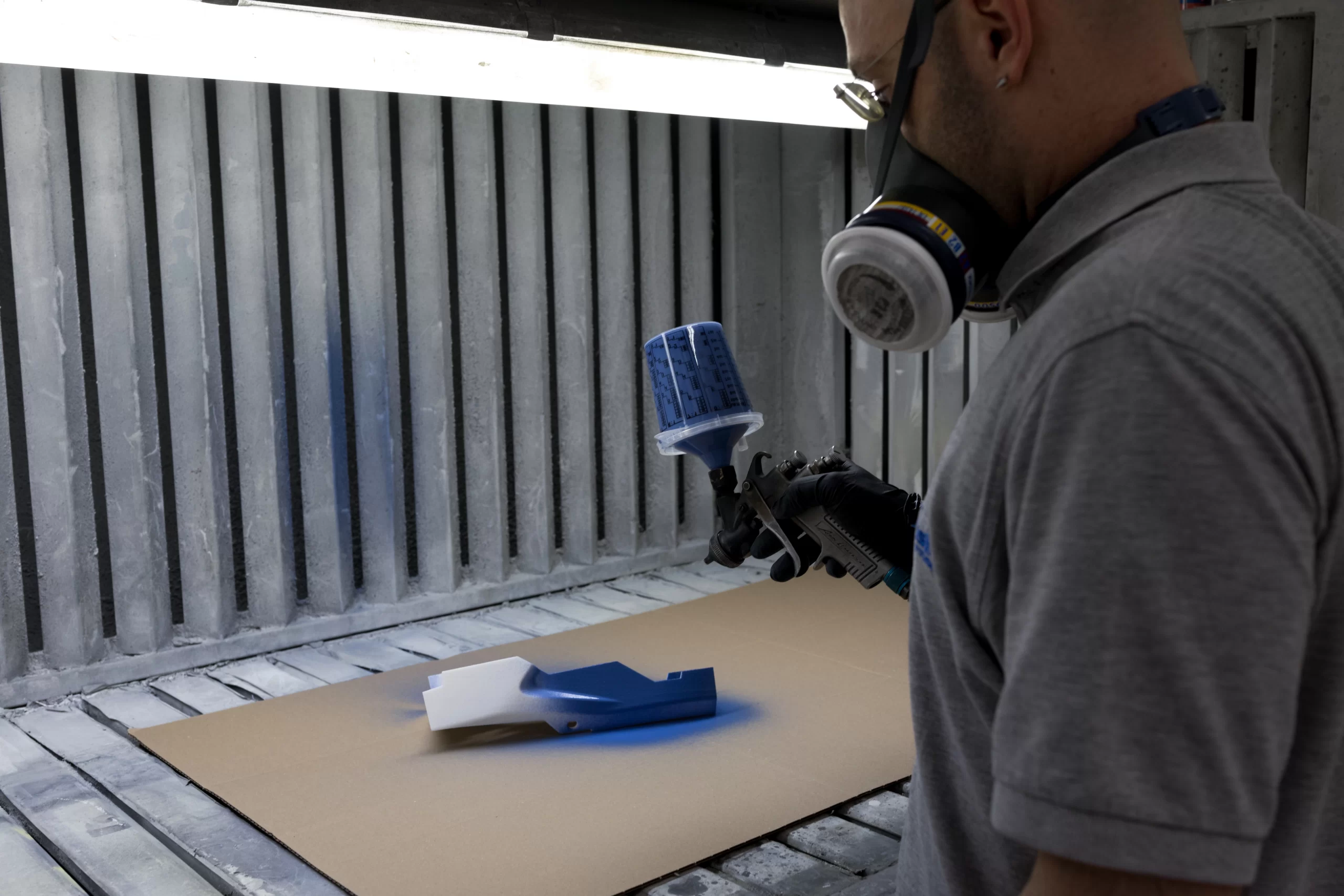
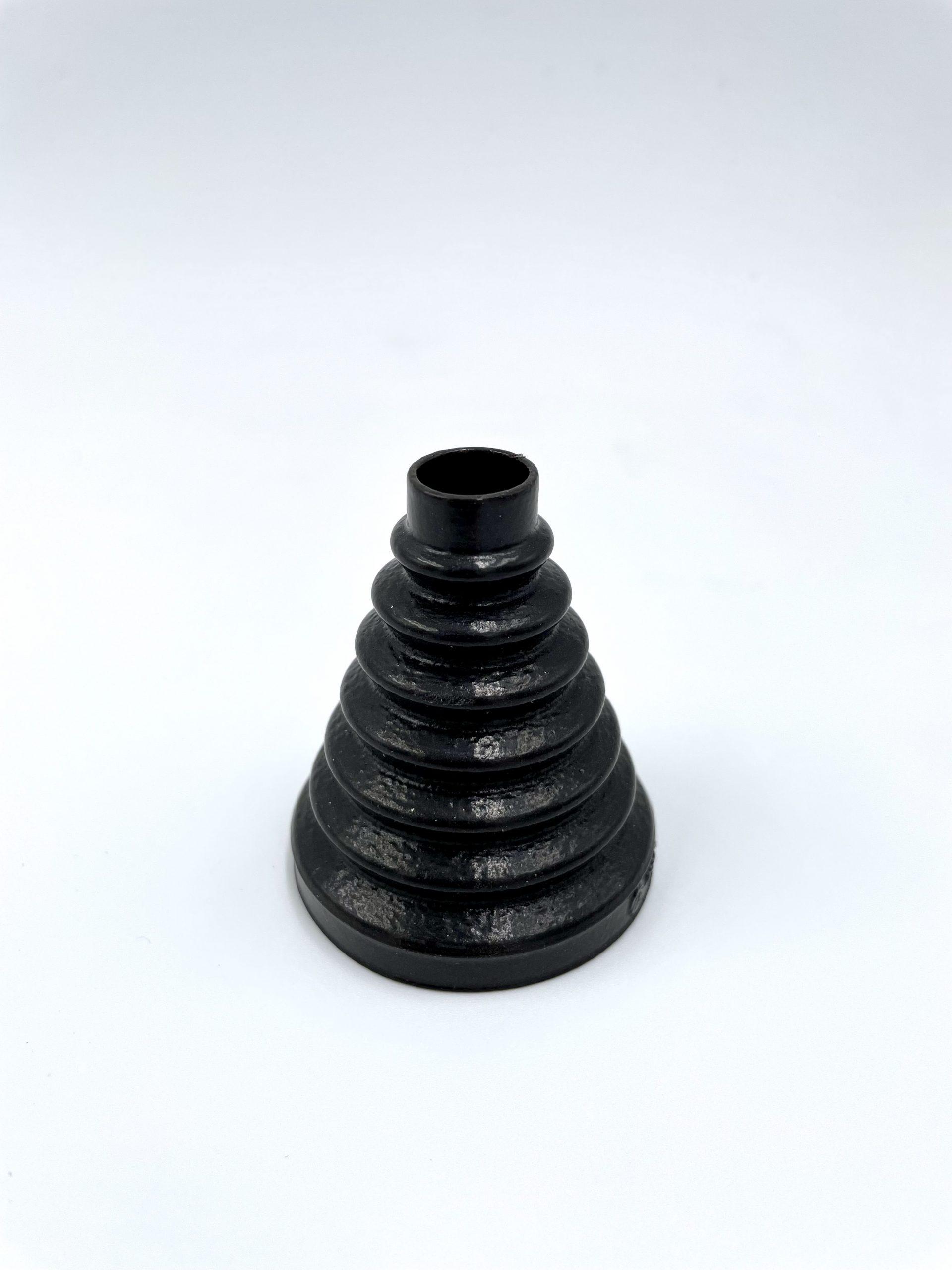
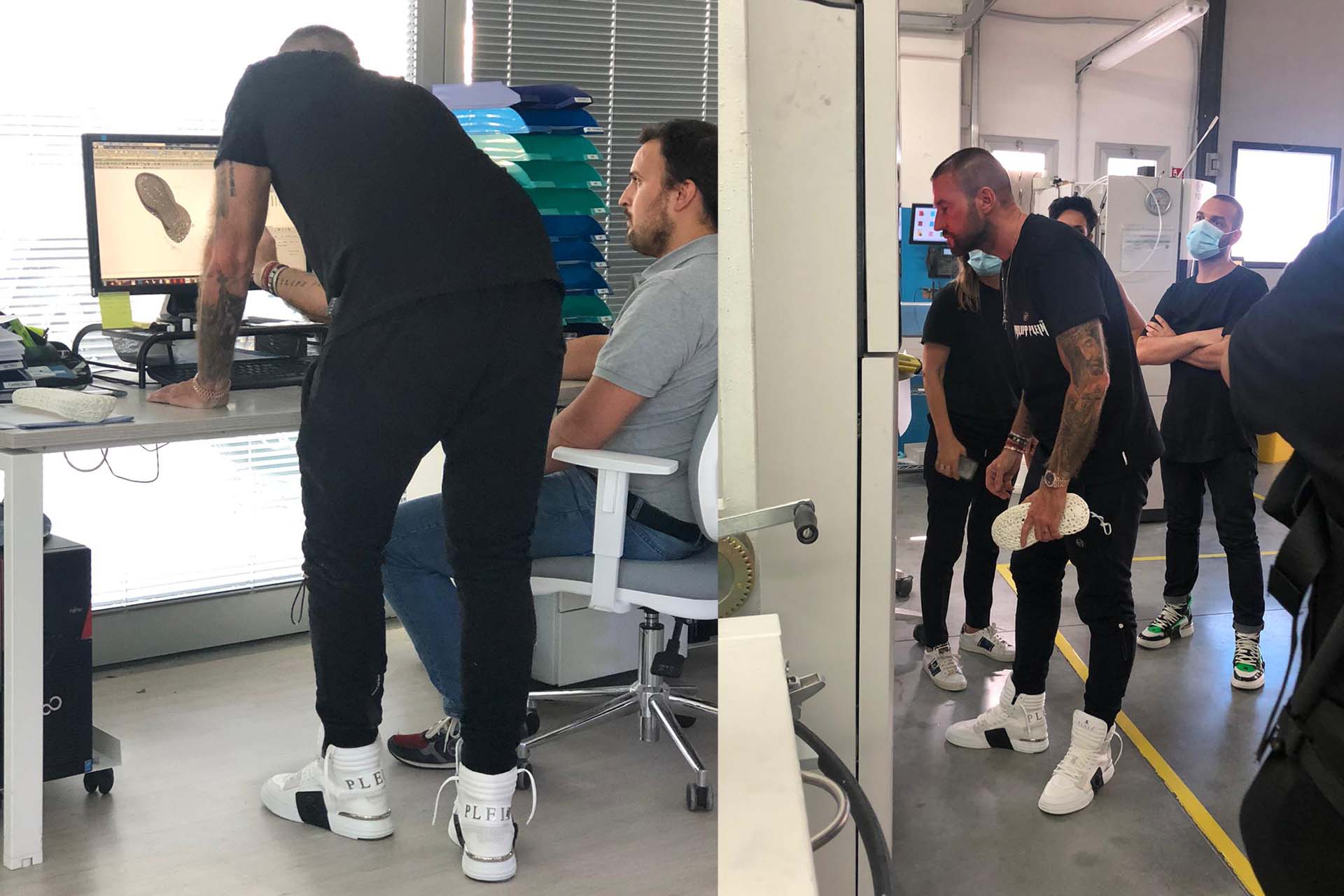
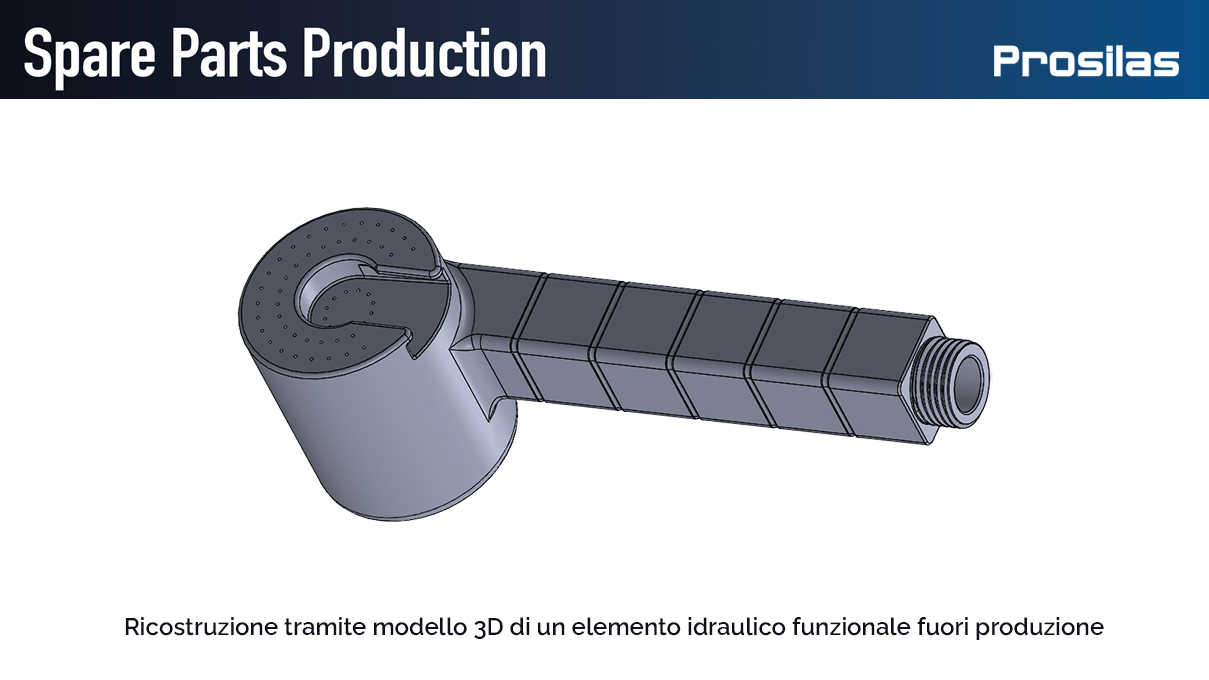
A process that we at Prosilas know well and that through the use of our 3D scanners and the application of reverse engineering has allowed us to produce a particular model of hydraulic tap breaker and a shower customized to the specific request customer’s.
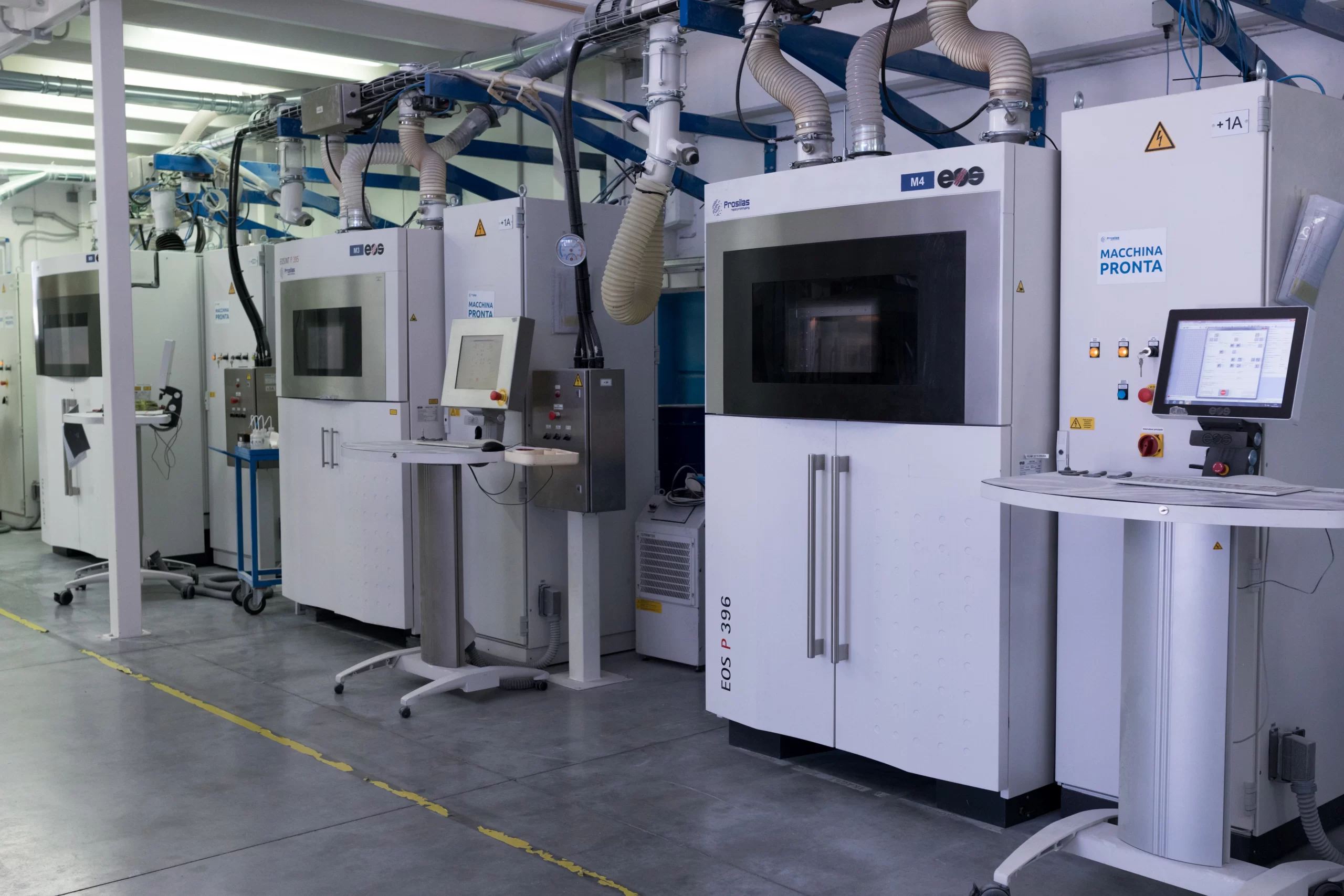
With the 3D file from the scanning of the part out of production, the SLS technology used in our laboratories Prosilas allows to 3D print functional elements, also offering the possibility to work on large results or series (working chamber 680x380x540 mm), being able to choose from a wide range of materials: PA12, PA12+Glass spheres, PA12 + Carbon fiber, PP (Polypropylene).
An opportunity, that of putting back on the market spare parts out of production getting the reconstruction through additive technology, that not only allows to answer to a specific need without looking for solutions of fortune or sketched, but which makes the production itself much more sustainable and performing.
On-demand warehouse
The case of the 3D reconstruction and printing of the tap and a custom shower model shows how on the one hand 3D printing allows to have a production according to the needs, thanks to a virtual warehouse on demand without the need to manage a physical storage and from the other offers the opportunity to rethink the component in additive, in order to obtain an improvement of the mechanical performances.
Innovative and customized additive solutions that we propose, supporting companies in all sectors, even those universally recognized as the most demanding just like the world of hydrothermohydraulics.
Read more on Prosilas
What is an STL file?
Lube Volley and Prosilas together to win, with the support of 3D printing
Lube Volley + Prosilas Case History What Prosilas and Lube Volley have in common is not only their...
Prosilas, Quality goes through the metrology lab
a laboratory where measurements are made on instruments and materials for compliance with standards and production of certificates.