Technologies
The right technologie for every application
3D Printing, Vacuum Casting, and Injection Molding
We are a unique service that integrates across all technologies – from additive manufacturing to vacuum casting, from injection molding to tooling.
Additive Manufacturing
Additive manufacturing, also known as 3D printing, is a revolutionary production process that creates three-dimensional objects by adding layer-by-layer materials, enabling complex designs, rapid prototyping, and reducing material waste.
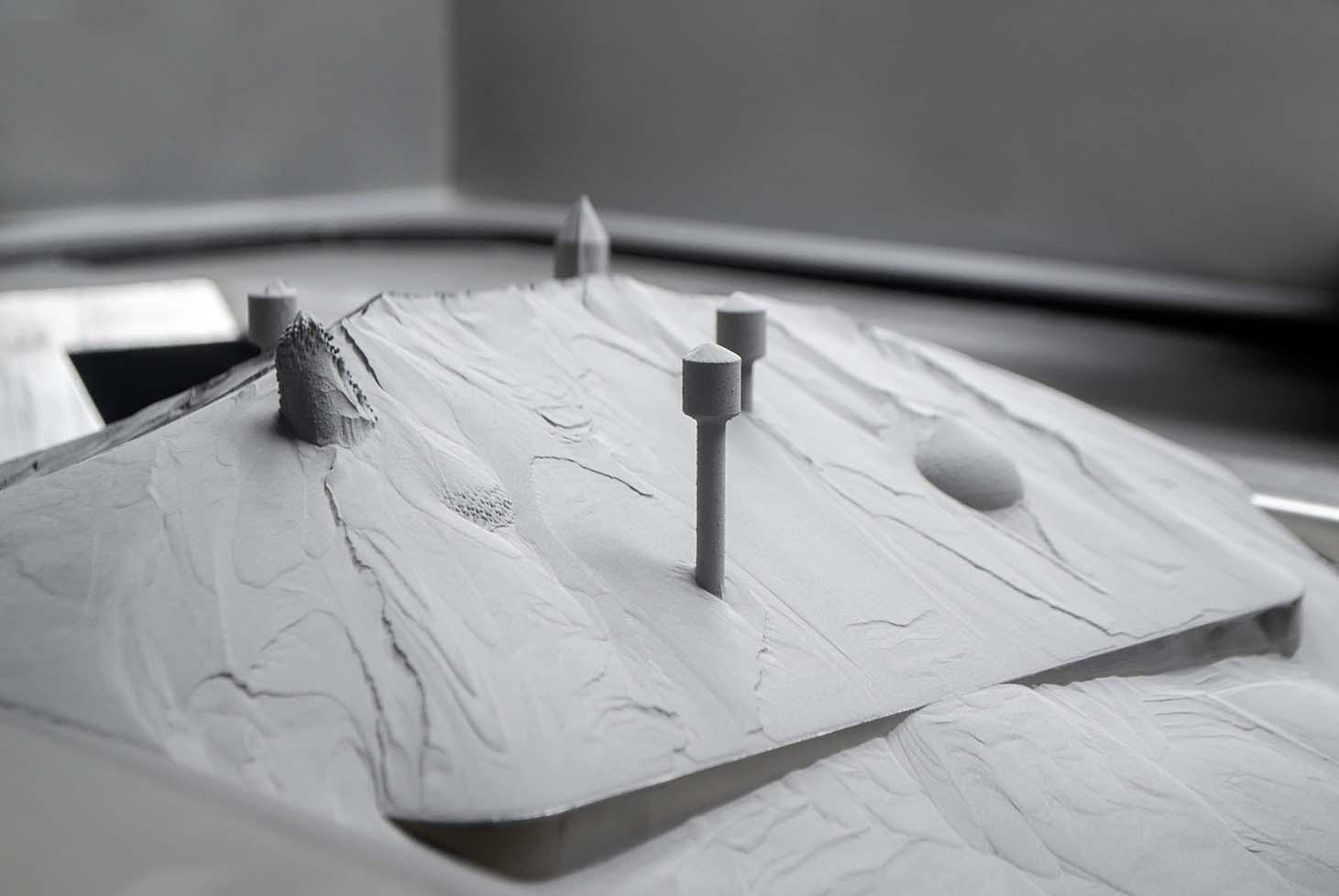
SLS
Selective laser sintering
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) is an additive manufacturing technology based on powder bed fusion ( PBF).
SLS technology uses powders with controlled particle size as a production material that is deposited evenly within the machine chamber.
The printing materials are melted by the application of thermal energy provided by a high-power laser that allows to sinter the particles layer by layer locally.
SLS technology is widely used in the field of rapid prototyping for the creation of highly complex design objects that also require good mechanical properties.
It is also used in the production of high print volumes thanks to the high productivity compared to other additive manufacturing techniques, allowing to increase the efficiency and reduce the post-process costs.
Printers
5 EOS P770 (680x370x540mm), 3 EOS P396 (300x300x600mm), 2 EOS P395 (300x300x600mm), 1 EOS 110 FORMIGA (190x240x300mm)
Materials
PA 2200,PA12 ALU , PA 603 CF , Hyper-Light Carbon, PA12 GF , PA2210 FR, Polypropylene, PA6 , TPU Black/White, PEEK ,PA 11
SLA
Stereolithography
Stereolithography (SLA) is a 3D printing technology based on the photopolymerization of a resin contained in a tank, through the action of a laser beam that emits ultraviolet radiation.
Prosilas uses SLA technology for rapid prototyping of 3D products that require complex geometries, high precision and best surface quality.
SLA 3D printed parts have excellent aesthetics and can easily be subjected to several surface finishes such as painting and metallization using a galvanic process.
With SLA technology, different resins can be used depending on the purpose of the prototype. Thanks to the high details and excellent surfaces of this technique, it is possible to produce test parts for wind tunnels, masters for silicone molds or to print transparent objects for prototyping car lenses and lights.
Printers
DWS 029X
Materials
Transparent Resin, Rubber-Like Resin, ABS- Like Resin, High Temperature Resistant Resin
Start a project
The Prosilas Staff will respond promptly by sending a detailed estimate with costs and delivery times.
FDM
Fused deposition Modeling
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) is an additive manufacturing technology that creates objects by depositing a filament layer by layer from a printing nozzle.
FDM technology can be used with a wide range of standard thermoplastic polymers.
You can create basic proof-of-concept models and provide a rapid prototyping service, taking advantage of low production costs.
FDM printed parts are resistant to heat, chemicals, mechanical stress and environmental variables thanks to their very high resistance and excellent thermal stability of the materials supplied by Prosilas.
The characteristics of durability and strength of the parts make FDM one of the most popular technologies for the production of objects for the aeronautical, aerospace and motorsports sectors.
Materials
Ultem 1010, Ultem 9085, ABS Polycarbonate, Polycarbonate, ASA


Polyjet
Polyjet fusion
PolyJet technology allows to manufacture items in a wide range of different materials. It is even possible to combine different materials in the same product – something unique to this technology. In addition, you can print more than 360,000 colour combinations with PolyJet. You can also obtain a transparent part using this method.
The technology involves curing an acrylic-based liquid layer-by-layer under a UV light. It is a speedy technology, and with this method you can build models in anything from soft rubber to hard plastic. You obtain a good level of detail, making the technology ideal for e.g. prototypes. Because you can in fact use different materials in the same print-run with this method, you can produce items with different properties but still of the same product.
The maximum dimensions for printed parts are 390 mm x 490 mm x 200 mm.
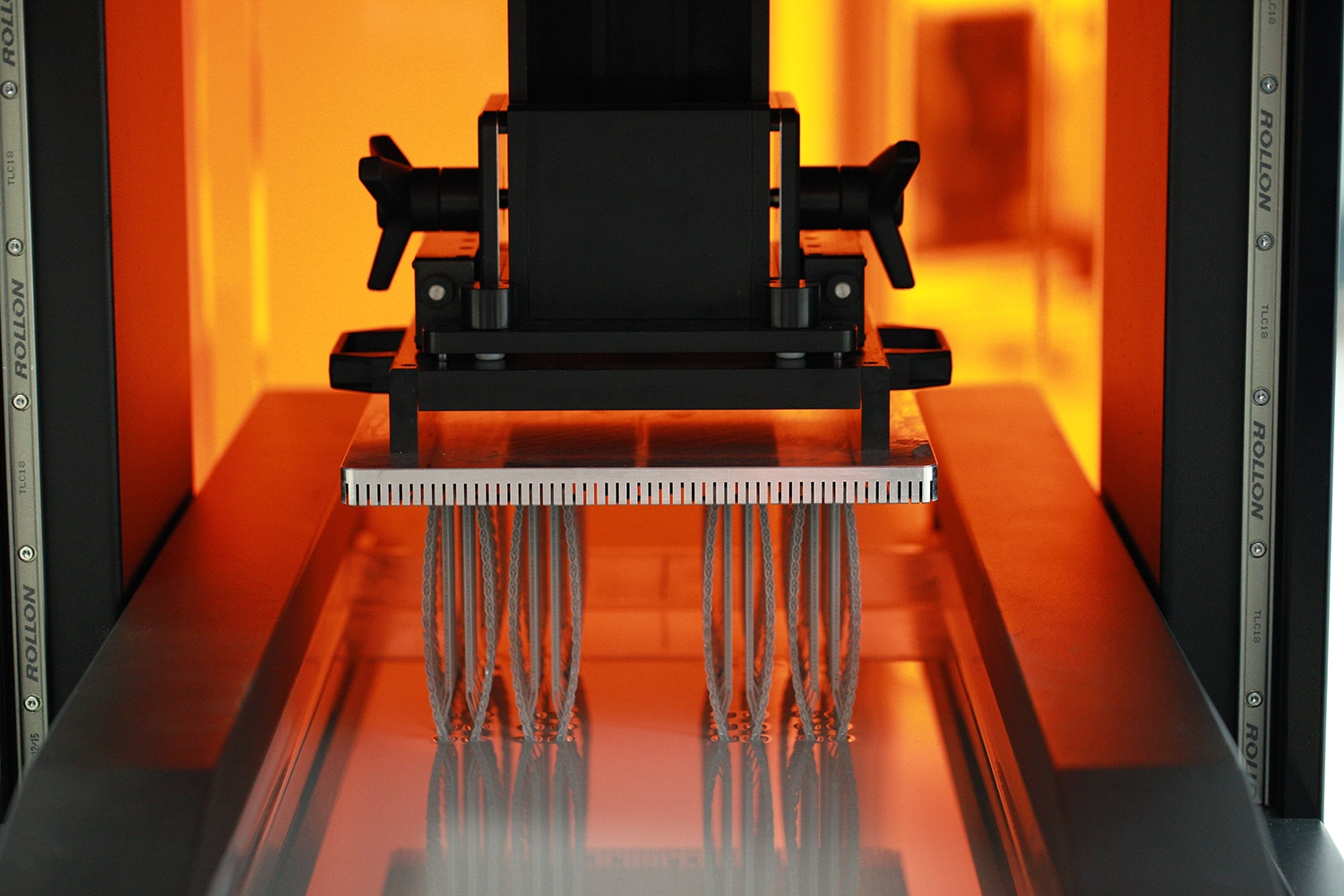
MJF
Multijet fusion
Just like SLS technology, MJF lays down material in powder form with a thickness of 0.08 mm.
Then, a “fusing agent” is applied where the material is to be fused and a “detailing agent” is applied on areas which are not intended for fusion.
Then energy in the form of heat is added, which makes the powder fuse where the fusing agent has been applied. The process is subsequently repeated with a new layer of powder.
Its amazing speed and resolution set a new standard for what is possible in 3D printing

DMLS
Direct metal laser sinteting
Direct laser sintering of metals (DMLS) or selective laser melting (SLM) are additive technologies for manufacturing metal parts.
Similar to SLS, DMLS/SLM techniques are based on the concept of powder bed fusion (PBF). With DMLS/SLM, metal 3D parts are printed starting from a raw material in powder that is sintered or melted.
Parts made with DMLS/SLM have mechanical properties equal or superior to those built with traditional techniques and can be used in the field of rapid prototyping, or as final components for series production.
Both technologies offer remarkable precision and the materials are suitable for many post-processes, such as CNC machining, heat treatments, both aesthetic and functional surface treatments/ performance.
Materials
AlSi10Mg, AlSi7Mg0.6 Aluminium, Ti6Al4v Titanium, Stainless Steel AISI316L , Maraging Steel
Start a project
The Prosilas Staff will respond promptly by sending a detailed estimate with costs and delivery times.
Traditional Technologies
The best equipment to offer the right solution for each application. 100+ machines for traditional production in order to provide the most complete offer for the production of polymer parts. We follow the life cycle of the product from prototypes to full-scale production.
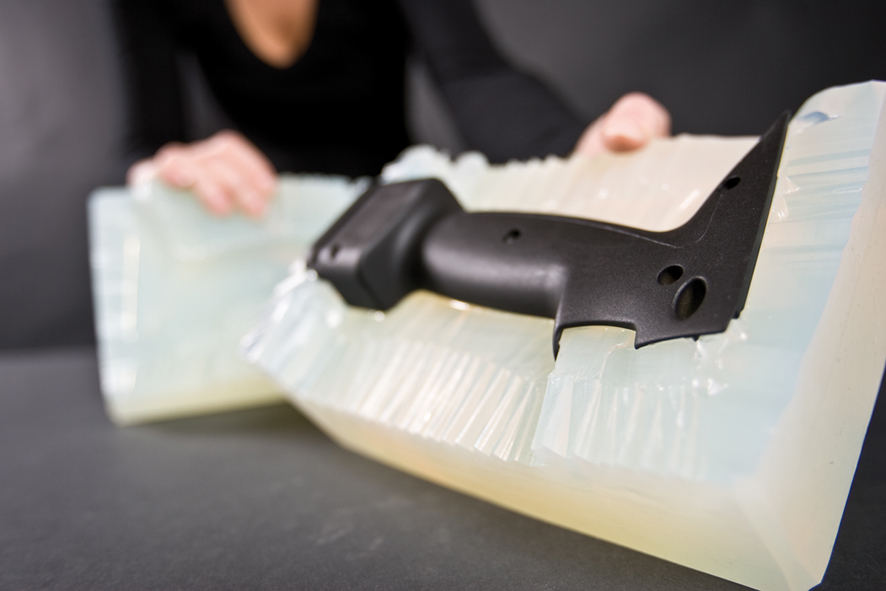
Vacuum Casting
Prosilas uses the vacuum casting technique (vacuum molding of polyurethane resins inside silicone moulds) to provide objects with complex geometry in small series for testing, maintaining excellent details, good mechanical characteristics and excellent surface quality.
A molded master is created using SLA technology to ensure a good surface to replicate, from which a silicone mould is obtained. To make the replicas of the object, the material is then vacuum-sealed inside the mould.
In development projects, there is often a need to undertake functional testing of the final design early on, using materials that simulate the plastic of the final construction. By producing casting moulds from silicon, parts can be cast in polyurethane (PUR) with the required properties.

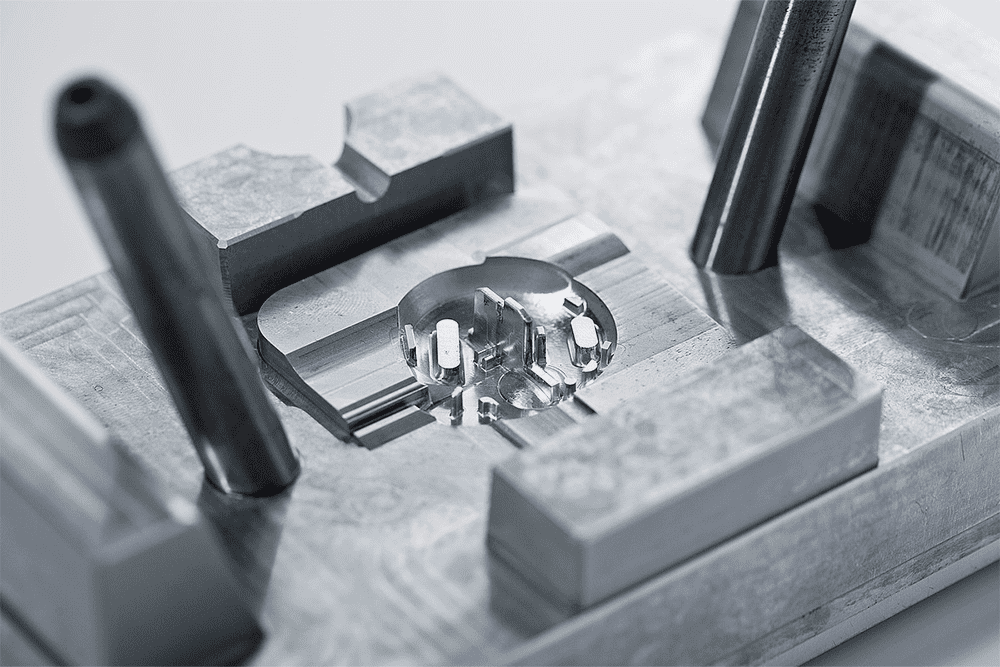
Injection moulding
Injection moulding is a manufacturing process for producing parts by injecting molten material into a mould.
Prosilas can scale production to meet customer demand. We have more than 110 automated injection moulding machines available to make every type of product. Moreover, before the manufacture, we simulate the injection moulding so that we can detect any defects and risks with the fabrication at an early stage.
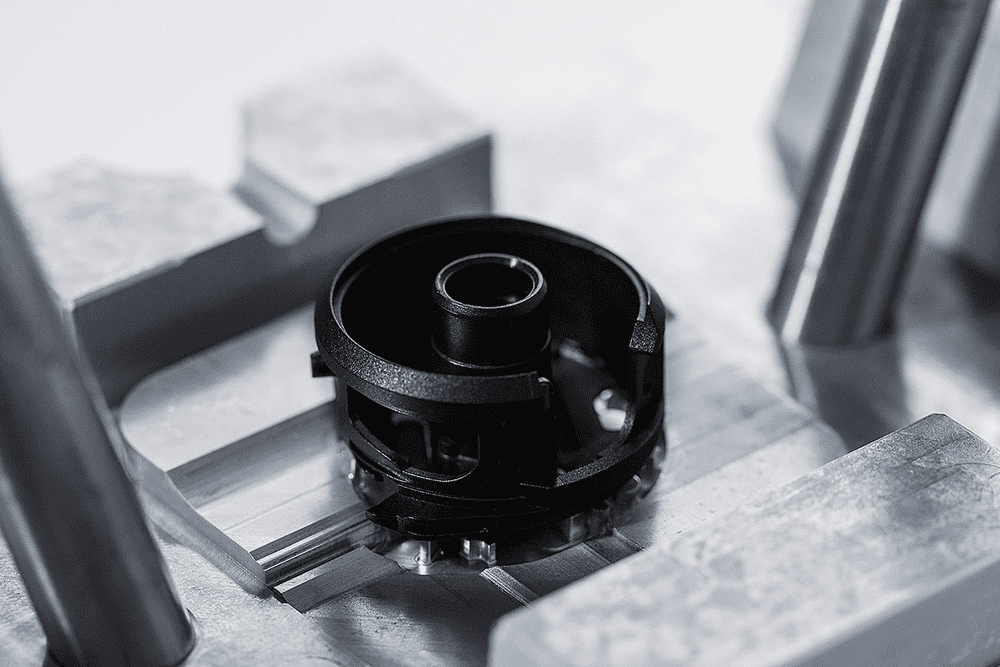
Machining/Tooling
CNC machining is a subtractive production process: a block of plastic material is machined by sharp rotating tools, removing the material to obtain an object.
Prosilas uses CNC to finish SLS parts if it is necessary to supply components with tight tolerances, above additive manufacturing standards, to ensure dimensional compliance or precise surface roughness.
It can also be the best option when some large, low-cost products, specific materials, or high-precision components are needed.
Lamination of composites
Lamination is a 3D printing technique that involves the arrangement of layers of carbon fiber or glass in a mould in order to obtain a shape.
The mould is then placed in autoclaves where the material is cured by temperature and controlled pressure.
The process of lamination guarantees very high quality and mechanical standards for the production of parts in aerospace, automotive and motorsports.
MATERIALS: Carbon fibre, Fiberglass
