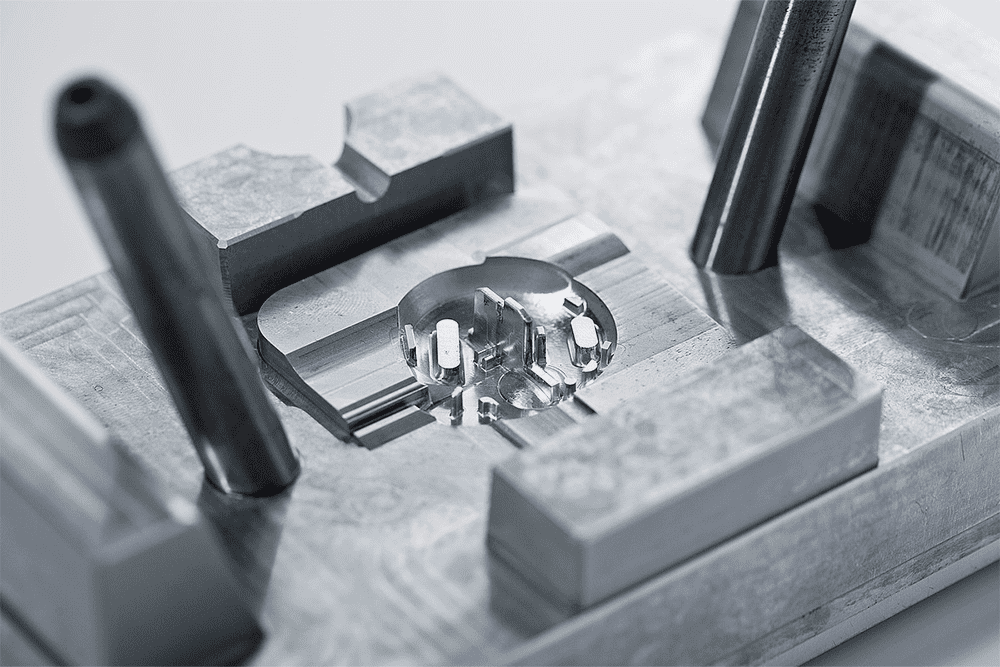
Tooling
At Prototal Prosilas, security and quality are at the core of our manufacturing process. We design and produce tools tailored to your specific needs, ranging from simple aluminum prototype moulds to high-volume hardened steel tools. By also handling the injection moulding process, we maintain full control over the entire workflow—from order placement to final delivery.
Before production begins, we conduct advanced injection moulding simulations to identify potential flaws and structural risks early on. Once the tool is designed, you receive access to trial samples and detailed process reports, ensuring a seamless transition from development to production.
Reliability brings peace of mind.
Prototal Prosilas: Explore the Possibilities of tooling
Our tools are precisely tailored to your specific requirements, offering a wide range of customization options. This includes various inlet types such as edge, rod, snout, tunnel, film, or hot runner systems. To achieve the ideal surface texture for your injection-moulded parts, tool surfaces can be ground, polished, blasted, spark-eroded, or etched.
We also provide overmoulding tools and true 2K tools for components that require multiple materials.
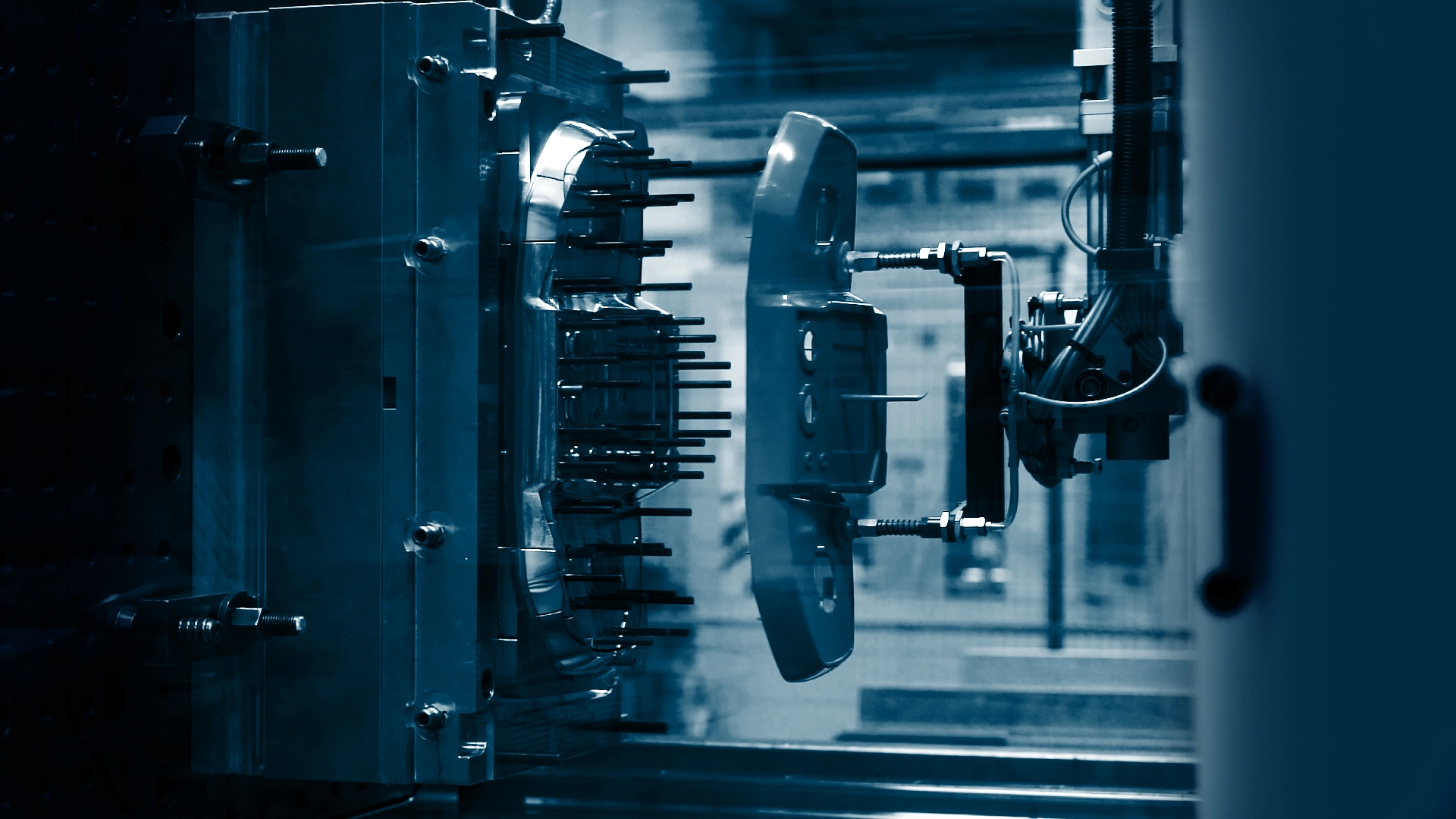
Once the tools are assembled, they undergo a test run to ensure accuracy and functionality. Following this, trial injection moulding begins using our in-house injection moulding machines, guaranteeing seamless integration into production.
Types of moulds for injection moulding
🔹Prototype Tools – Aluminum
Our prototype tools are designed with a streamlined approach to match the required production volume. Manufactured in-house using aluminum, these tools enable a fast and efficient production process while keeping investment costs to a minimum. Components can be injection-moulded under production-realistic conditions, typically yielding around 100 parts.
🔹 Low-Volume Tools – Aluminum
Designed for a more automated injection moulding process, our low-volume tools are also produced in-house using aluminum. This ensures a cost-effective and efficient workflow while maintaining production-realistic conditions. With a lifespan of up to 100,000 shots, these tools support the manufacturing of a substantial number of components, bridging the gap between prototyping and full-scale production.
🔹 High-Volume Tools – Steel
For large-scale production, our high-volume tools are made of steel and sourced from trusted external suppliers. Throughout the process, our project team closely monitors timelines to ensure seamless execution—from tool design approval to trial sample measurements and tool adjustments. By adhering to strict tooling standards, we guarantee high efficiency and precision. Once finalized, the tools are transferred to our facilities for the production of final trial samples, ensuring a smooth transition into full-scale manufacturing.
Start a project
The Prosilas Staff will respond promptly by sending a detailed estimate with costs and delivery times.
FAQs

What is the Difference Between Aluminum and Steel Tools?
The primary difference between aluminum and steel tools lies in their lifespan and application.
Aluminum Tools
- Faster Production & Cost Efficiency – Aluminum tools are lighter and can be machined more quickly in our milling machines, often providing cost advantages.
- Ideal for Prototypes & Low-Volume Production – Due to their shorter lifespan, aluminum tools are best suited for prototypes and small production runs.
- Superior Heat Conductivity – Aluminum distributes heat more evenly within the mold, reducing cycle times and improving efficiency.
- Limitations – Being a softer material, aluminum wears out more quickly, especially when used with glass-fiber-filled materials.
Steel Tools - High Durability & Wear Resistance – Steel tools are designed for long production runs and can withstand high pressures and temperatures.
- Best for Large-Scale Production – Their strength makes them ideal for high-volume injection molding, particularly with glass-fiber-reinforced or high-temperature materials.
- Longer Manufacturing Time & Higher Cost – Steel tools take longer to produce and are more expensive due to their durability and complexity. They are also larger and heavier compared to aluminum tools.
- Choosing between aluminum and steel tools depends on your production needs, balancing cost, speed, and longevity to achieve optimal manufacturing efficiency.
When Should I Choose Aluminum Tools? When Should I Choose Steel Tools?
The choice between aluminum and steel tools depends on your specific production requirements.
Choose Aluminum Tools If:
- You need a quick turnaround and shorter lead times.
- Your production volume is low to medium, such as prototypes or small series.
- Cost efficiency is a key factor.
- You require good heat conductivity for faster cycle times.
Choose Steel Tools If:
- You need high durability and long-term wear resistance.
- Your production volume is high or requires extended tool lifespan.
- You are working with glass-fiber-filled or high-temperature materials.
- You need tools that can withstand higher pressures and temperatures.
Not sure which tool is right for your needs? We’re here to help! At Prototal, we have extensive expertise in tooling and can guide you in selecting the best solution for your production process. Contact us to find the perfect fit!
The Work Process Before Production Begins
To ensure high-quality and efficient manufacturing, we follow a structured process before producing parts.
1. Analysis
We begin by simulating the injection molding process to identify potential design issues and risks early on. Any necessary modifications are implemented, followed by a new simulation. This approach minimizes the number of adjustments required, reducing costs and ensuring a smoother production process.
2. Design
Aluminum Tools: Our in-house tool designers create and optimize the design for cost-effective manufacturing.
Steel Tools: Designed by our trusted suppliers according to our specifications, subject to our approval.
3. Manufacturing
The tools undergo milling and spark erosion to achieve the required precision. Automated systems and robotic handling ensure an efficient and streamlined production process.
4. Assembly
The tools are assembled and finalized, with surface treatments such as blasting, grinding, or polishing applied to achieve the desired finish. A test run is conducted before injection molding to verify the tool’s accuracy.
5. Verification
The tool is tested through an initial injection molding process, producing trial samples. We verify injection parameters and ensure compliance with customer specifications. Documentation, including measurement protocols and PPAP, is provided as agreed with the customer.
Guidelines for Tooling Selection
Several factors influence the design and manufacturing of the tool, ensuring optimal performance and cost efficiency.
1. Material Selection
- The chosen material affects shrinkage compensation, which must be accounted for in the tool design.
- Different materials impact tool lifespan, especially when using abrasive or high-temperature materials.
2. Early Involvement for Quality Optimization
- Engaging us early in the project allows for product reviews and design adjustments, optimizing components for quality-assured manufacturing.
3. Production Volume & Tooling Strategy
- The number of components to be produced determines the tooling approach:
- Prototypes – Quick turnaround with cost-effective aluminum tools.
- Low Volumes – Balance between efficiency and cost.
- High Volumes – Durable steel tools for long production runs.
- Number of mold cavities – More cavities increase tool cost but lower per-unit component cost.
4. Tool Complexity
- Design Complexity – Features such as multiple ribs can affect tool design and manufacturing.
- Undercuts – If required, the tool must be designed accordingly.
- Encapsulated Components – Special tooling considerations may be needed.
5. Surface Finishes
- The required surface finish impacts tooling processes, with options including:
Milled, ground, polished, blasted, spark-eroded, or etched surfaces.
6. Gating & Aesthetic Considerations
- Gating point visibility – Should the gate be concealed or is a visible gating point acceptable?
By considering these factors early on, we can ensure the best tooling solution for your specific production needs.
